Operating Environment
Material Matters
The COVID-19 global pandemic has reshaped many aspects of the business environment, compelling organisations to transform to stay profitable and relevant. Sustaining success during turbulent times requires fresh analysis, nimble adaptations of strategies and business models, and creativity in confronting challenges and seizing new opportunities presented by the changing environment.
Figure - 06
In adapting the Bank’s strategy to face this ‘new normal’, the Bank analysed its external environment to identify matters arising from changes that were brought about by the pandemic and emerging trends that were relevant to key stakeholder groups, as given below:
| Political | Economic | Social | Technological | Environmental | Legal/Regulatory | |
Investors |
1. Lack of desired level of policy consistency |
2. Economic slowdown due to pandemic |
3. Growing influence of social media | 4. Unorthodox competition and financial disintermediation | 5. Directions and guideline to counter impacts of the pandemic | |
| 6. Lack of desired level of transparency and accountability | 7. Depreciating currencies against USD |
8. Demand for non-financial information and long termism |
9. Compliance with new Basel requirements | |||
| 10. Downgrading of the Sovereign rating and its cascading effect on the Banking industry | 11. Demand for more transparency and accountability | 12. Higher regulatory capital | ||||
| 13. High CAPEX requirements | 14. New Banking Act | |||||
Customers |
15. Envisaged upturn in private sector credit and improvement in asset quality | 16. Changing customer expectations | 17. Migration towards digital platforms | 18. Compliance requirements and regulations such as FATCA1, GDPR2, and BEPS3. | ||
| 19. Import restrictions | 20. Cybersecurity threats | |||||
Employees |
21. Need to enhance productivity | 22. Staff recruitment and retention becoming more challenging | 23. Technology driving change in job skills | |||
| 24. Health and Safety | 25. New working cultures | |||||
Society and environment |
26. Geopolitical conflicts | 27. Declining worker remittances | 28. Need to commit to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) | 29. Increasing frequency and magnitude of natural disasters and poor disaster preparedness | ||
| 30. Corruption | 31. Declining global competitiveness of Sri Lanka | 32. Increasing conflicts | 33. Increasing demand for green banking and green lending | |||
| 34. Increasing drug pedaling and drug and alcohol addiction | 35. Pandemics hampering world trade and economy | |||||
Business partners |
36. A more collaborative approach | 37. New technological advances such as AI, Robotics, blockchain |
1-FATCA: Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act, 2-GDPR: General Data Protection Regulation, 3-BEPS: Base Erosion and Profit Shifting
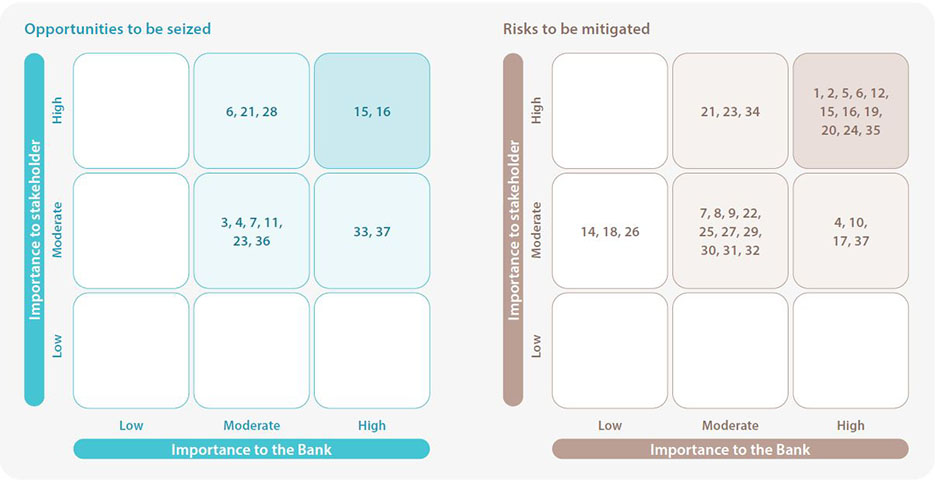
These trends present risks, opportunities or both and their impact is felt by the stakeholders and the Bank alike on varying degrees. The risks that presented from the pandemic outweighed the risks presented by other emerging trends and its impact was felt across all of our stakeholders at different magnitudes. The topics that stem from these trends and are material to the Bank according to their impact on stakeholders and the Bank itself are portrayed in the matrices that follow. The Bank defines material matters as those that significantly affect the Bank’s ability to create value over the short, medium and long term. Materiality of each matter is determined by its relevance, the magnitude of its impact, and the probability of occurrence. The pandemic is primarily responsible for the repositioning of topics by pushing them up or down the axes of the materiality matrix.
Following this study the Bank re-shaped its strategies to fit for the time and were then embedded in the Corporate Plan for execution by the Management together with underlying KPIs for measurement of successful implementation. Success in the Bank’s value creation journey under the four strategic imperatives is outlined in the section on Management Discussion and Analysis.
Management approach
The Bank manages its material topics through its strategic planning process by assigning responsibility to the heads of the relevant divisions of the Bank, allocating necessary resources based on the significance of each material topic towards achieving the aforesaid strategic imperatives. Goals and targets, where relevant are embedded into the KPIs of the Key Management Personnel to ensure that the organisation achieves its objectives with regard to its material topics and are reviewed at regular intervals.
Many policies are in place guiding its people to conduct activities in a responsible, transparent, and ethical manner in managing the material topics. These policies are duly adopted by the Board of Directors and are reviewed at predetermined intervals to stay current with the changing environment. Timely revision of these policies are monitored by the Integrated Risk Management Unit and is reported to BIRMC.
Where relevant grievance mechanisms are in place with assigned responsibility to the relevant divisional heads to manage, address and resolve grievances.
Screening is carried out into the social and environmental aspects of the Bank’s lending to its customers and dealings with its business partners.
Internal and external auditing and verifications are carried out to ensure that the internal controls, policies and procedures laid down to achieve the objectives of material topics are adhered to. Findings are reported to the Board of Directors and/or to the respective Management Committees on a periodic basis for information and corrective action where necessary.
The effectiveness of the management approach is amply demonstrated by the awards and accolades received by the Bank over the years.
Material matters
Table - 05
| Material topic | GRI Disclosure | |
| 1 | Lack of desired level of policy consistency | GRI 201: Economic Performance GRI 203: Indirect Economic Impact GRI 207: Tax |
| 2 | Economic slowdown due to pandemic | |
| 4 | Unorthodox competition and financial disintermediation | |
| 5 | Directions and guideline to counter impacts of the pandemic | |
| 6 | Lack of desired level of transparency and accountability | |
| 10 | Downgrading of the Sovereign rating and its cascading effect on the Banking industry | |
| 12 | Higher regulatory capital | |
| 15 | Envisaged upturn in private sector credit and improvement in asset quality | |
| 16 | Changing customer expectations | |
| 17 | Migration towards digital platforms | |
| 19 | Import restrictions | GRI 201: Economic Performance |
| 20 | Cyber security threats | GRI 418: Customer Privacy |
| 21 | Need to enhance productivity | GRI 404: Training and Education |
| GRI 405: Diversity and Equal Opportunity | ||
| 23 | Technology driving change in job skills | GRI 404: Training and Education |
| GRI 405: Diversity and Equal Opportunity | ||
| 24 | Health and Safety | GRI 403: Occupational Health and Safety |
| 28 | Need to commit to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) | |
| 29 | Increasing frequency and magnitude of natural disasters and poor disaster preparedness | GRI 302: Energy |
| GRI 305: Emission | ||
| 33 | Increasing demand for green banking and green lending | |
| 35 | Pandemics hampering world trade and economy | |
| 37 | New technological advances such as AI, Robotics, blockchain |