Management Discussion and Analysis
Leading Through Innovation
That we have been living through a digital revolution over the last few years is self-evident. Conventional business models and ecosystems are being rapidly transformed, and the rate of technological change and the rush of new, agile, entrants to the financial landscape has intensified competition and risk. The Bank has welcomed these challenges as a trigger for meaningful innovation, spurring it to emerge as a pioneer in the digital banking space.
In 2020, one side effect of the COVID-19 pandemic is that it has acted as a catalyst for digitalisation out of necessity, and has accelerated the pace of digital change and adoption. During April-May, when the entire country was on a lockdown and banking was made one of the essential services in the country, demand for continuity of service through digital channels escalated. The initiatives and investments the Bank has made over the last five years in building its digital ecosystem – its portfolio of customer facing platforms, digital products, and services, as well as back-end processes and infrastructure – provided it with a strong foundation to meet these new challenges.
The pandemic has also served to expose limitations and areas of weakness in the current digital banking space. Despite the strides made towards building a digital banking ecosystem, the mass demand for increased digital services makes it clear that there is much work to be done both within the Bank and in the wider landscape. From the opening of new accounts, to
on-boarding customers to digital platforms, to applications for loans, to authorising identities, the system is still very reliant on the brick and mortar model. Existing KYC and AML policies, for example, typically require face-to-face identity verification for customer onboarding, which became challenging under the circumstances. But the response of the Bank in its digital initiatives and the CBSL in relaxing regulations (such as in-person KYC) are all positive developments that augur well for the future.
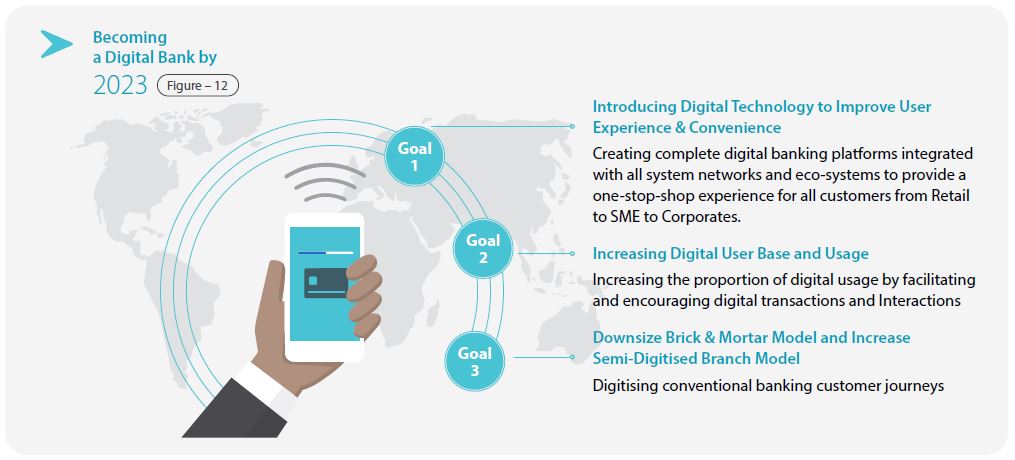
Digital Roadmap up to 2023
The Bank has set its sights on three Digital Goals for 2023:
Accordingly, the Bank will continue to invest in redesigning its conventional banking processes as digital processes, integrating with other ecosystems (such as connecting with internal workflows for less manual intervention), and upgrading internal systems to be ready to adapt to anticipated changes in the regulatory environment (open APIs, digital KYC, etc.) and risk management. The Bank is also placing an emphasis on ‘developing the future bank’, i.e. re-skilling staff and attracting specialised talent, building further partnerships, and developing its data analytics capabilities.
Investments in IT infrastructure
Table - 17
| Indicator/Year |
2020 Rs. Mn. |
2019 Rs. Mn. |
2018 Rs. Mn. |
2017 Rs. Mn. |
2016 Rs. Mn. |
| Investments in Hardware (Computer Equipment) | 505.742 | 567.689 | 1,034.115 | 791.165 | 620.541 |
| Investments in Software (Licenses etc.) | 409.322 | 387.432 | 333.181 | 449.354 | 416.816 |
In the year under review, digital onboarding of existing customers grew at 140.17%, a 22.47% increase over the general trend over the last two years. The Bank also introduced 100% digital onboarding for new customers via its groundbreaking Flash app, adhering to the CBSL guidelines for digital KYC during the lockdowns.
Migration to digital channels
Table - 18
| Indicator/year | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 |
| Digital Adoption (Existing Customer Onboarding) | 333,941 customers (140.17% YoY growth) | 139,040 customers (110.21% average YoY growth) | 66,143 customers (39.92% average YoY growth) |
| New Customer acquisition/ Onboarding (Digital KYC) | 9,680 customers | N/A | N/A |
| Percentage of total customer transactions conducted digitally | 31.75%* | 32.18%* | N/A |
*Average Figure obtained
ComBank Digital
Currently, the Bank’s online platform stands as the most subscribed online platform in the country. During the year under review, the Bank integrated online and mobile banking channels on a single omni-channel platform with the launch of “ComBank Digital”, powered by Fiserv, the US-based global provider of financial services technology. Another industry first, ComBank Digital brings together all the Bank’s digital banking channels, including online banking, mobile banking app, and mobile (WAP), on a new, highly-secure, user-friendly, responsive web application catering to both retail and corporate users. ComBank Digital is not only more vibrant and elegant, but features a range of built-in options that allow users to self-manage their digital banking preferences, thus offering an unparalleled level of functionally and customisability. This moves the Bank closer to its digital ethos of greater segmentation and granularity, enabling unique user experiences.

ComBank Digital launch - Email
Standard services such as checking balances of current, savings, investment, loan, and credit card accounts, Fixed Deposits investments, Personal Loans and Housing Loans, investing in Treasury Bills and effecting payments for share trading can all be carried out securely via ComBank Digital. The platform effects all transactions between user accounts, third-party Commercial Bank accounts, and accounts in other banks on a real-time basis, and supports bill payments to about 70 entities in nine categories such as telephone, electricity, water, credit cards, insurance, Pay TV, education, school fees and rates. Additionally, the Bank has also been successful in accommodating income tax payments to the Inland Revenue Department on this platform. This platform places the Bank at the forefront of the digital banking space.
Combank Digital has been launched in the Maldivian market and is expected to be rolled out in Bangladesh in 2021. Additionally, the Bank plans to make this app tri-lingual (for Sri Lankan operations), and include Bengali (for Bangladesh customers) and Divehi (for Maldivian customers) options in the near future. The Bank also introduced an umbrella app that houses the full suite of the Bank’s mobile apps on our customers’ phones.
Total Financial Transactions Initiated Through Digital Channels
Table - 19
| Volume | Value | |
| 2019 | 25,741,711 | Rs. 1,822.49 Bn. |
| 2020 | 33,959,505 | Rs. 2,411.39 Bn. |
| Growth | 31.92% | 32.31% |
Flash Digital Account
In 2020, Flash, the Bank’s ground-breaking, trilingual banking app, was upgraded with several features that are revolutionary in the local banking context, pushing the Bank further in its efforts to digitalise the customer journey. A QR Payment module was added to the app that enables Flash users to scan a Lanka QR code of any merchant to make payments direct from either Commercial Bank accounts or accounts with other banks. Subsequently, a QR code upgrade, made possible by the Bank’s partnership with PickMe and the integration of the respective apps of the two organisations, made it possible for Flash users to pay digitally for their rides on the PickMe ridesharing service. A partnership with with Tenaga Car Parks (Pvt Ltd) enabled users to pay for parking via the app at Tenaga managed on-street and off-street parking spaces without having to visit a payment booth or locate a fee collector.

CBSL recognised the Bank as an active supporter for LANKAQR initiative

Flash App Screen
This year, the Bank also introduced an advanced budgeting module to the Flash app that includes several tools that facilitate and promote personal financial discipline and management. The Flash Spend Tracker Module with a Payment Categorisation Option enables users to categorise their purchases. A dashboard presents an overall picture of a user’s spending habits and provides a downloadable history of monthly transactions in the form of an eStatement.
But the truly novel centerpiece of this module is the “Save the Environment” tool, which allows users to calculate the environmental impact of their spending. The Bank is the first company in the region and the fifth bank in the world to introduce a tool developed based on the leading climate impact index, approved by United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCC), the Aland Index 1.0. This tool analyses transactional data to estimate the carbon footprint of each transaction made through Flash in app payment options including through the Flash Debit Card and QR code scanning. This reveals to the user not simply financial costs, but the hidden environmental and social costs of the user’s consumption pattern. Understanding this data can help Flash app users to transform their habits or make choices to invest in the environment as a means of offsetting the impacts of their consumption.
Flash usage
Table - 20
|
Growth in 2020 % |
|
| YoY User base growth | 92.68 |
| YoY Usage growth | |
| Value growth | 468.52 |
| Volume growth | 323.31 |
|
Investments through Flash App (eFDs) |
up by 145.4 |
| Life insurance applications | up by 45.3 |
| Funds transfers | up by 354 |
| Bill Payments | up by 260 |
Combank Q+
During the year under review, the Bank was recognised by the CBSL for its pioneering efforts in enhancing the digital payments landscape of the country. In 2019, the Bank launched ComBank Q+, the first Quick Response (QR) based Payment App to be certified and launched under LANKAQR, which allows the entire debit and credit card base of the Bank to make QR payments. This year, the app was re-launched with new features to improve user experience. Both the Consumer and Merchant applications of ComBank Q+ were upgraded to include biometric authentication login and self-registration. Customers of the Bank can now pay a range of bills instantly via the app following the introduction of an In-App Bill Payments feature. Furthermore, the Bank became the first bank in Sri Lanka to enable its Credit Card holders to settle their Credit Card outstanding balance by scanning a QR code appearing on their monthly Credit Card statements. In yet another initiative, the Bank partnered with Mobitel to allow mCash merchants to accept QR code based payments from any mobile payment App registered under LANKAQR, with the transaction processed through the Q+ engine.

ComBank extends self-registration for online and digital banking
Online Payments
Within the burgeoning e-commerce sphere, the Bank has swiftly established itself as a market leader with its payment processing services now accounting for approximately two out of five transactions. This market share of 40% is a testament to the role the Bank has played in supporting the country’s retail industry and promoting online sales for customers. The Bank currently supports the online payment processing of over 500 merchants through MasterCard Payment Gateway Services (MPGS) and Visa Cybersource (launched by the Bank in Sri Lanka during 2020), two of the world’s leading payment gateway platforms that are fully-compliant with Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) requirements. The third IPG solution of the Bank, ComBank SimplePay, was also introduced in 2020. This product is a local adaptation of the MasterCard product Simplified Commerce, and provides local entrepreneurs and SMEs the opportunity to create their own online store.
IPG usage
Table - 21
|
2020 Annualised |
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | |
| IPG Volumes (Rs. Bn.) | 17.338 | 17.288 | 11.649 | 6.972 | 4.058 |
| YoY Growth Rate (%) | 0.28 | 48 | 67 | 72 | |
| IPG Merchants | 375 | 229 | 190 | 151 | 129 |
| YoY Growth Rate (%) | 63 | 21 | 26 | 17 | 48 |
Remit Plus
The Bank’s remittance app, ComBank RemitPlus, which was launched to commemorate International Migrant Day on December 18, 2019, was developed and upgraded in its first full year of use in 2020. Remittances from Sri Lankan expatriates is one of the country’s major sources of income. The Bank also upgraded the Blockchain based remittance channel, which the Bank launched in partnership with RippleNet, and expanded this service to South Korea and Middle East through further RippleNet partnerships.
Western Union (WU) Cash to Account was introduced in 2020 and is yet another example of how the pandemic acted as a catalyst for the technological progress of the Bank. WU Cash to Account was introduced during the lockdown period in the first half of the year to permit customers to claim WU cash remittances without visiting branch counters. Since then it has seen significant growth.
WhatsApp Banking
The Bank launched its WhatsApp banking solution in December 2020, and this product represents perhaps the easiest and fastest form of mobile banking. By sending a simple ‘Hi’ to a designated WhatsApp number, the user will receive a simple set of instructions on how to access several services including viewing account balance and account history, requesting a cheque book, information about fixed deposits, housing loans, and foreign exchange rates, and self-registration with ComBank Digital. Another crucial feature of this product is the ability for potential customers to complete registration to open a new account with the Flash app. This product is positioned as a simple pathway to the world of digital banking for customers that can subsequently lead to deeper and more sustained forms of digital engagement. Within just six weeks of use, the app has had 8,167 new registrations and 35,411 total transactions.
ePassbook
The Bank upgraded its ePassbook app to include features like self-registration, real-time transaction notifications, and biometric login, significantly increasing the flexibility of account management, user-autonomy and convenience. The app, which was introduced in 2016, was the first Digital Passbook in the Sri Lankan banking industry and remains the only mobile application of its genre to date.
Process Improvements
While the Bank’s efforts were concentrated on responding to the contingent and shifting situation brought about by the pandemic, it introduced several new automated processes focused on building robust back-end digital processes. Noteworthy developments include:
- Introduction of e-slips for cash and cheque deposits improved the customer turn-around time and also increased the accuracy.
- Through centralisation of Transfer Cheque process, the Bank managed to reduce operational cost through staff reduction at branches and improve the operating efficiency by speeding up the process.
- The automation of Post-Dated Cheque handling process, through which the Bank managed to increase the efficiency of a normally cumbersome process.
- Launched the Bank’s first ever Hyper Automation project to fully automate the User ID Management of the Bank using IBM BAW (Business Automation Workflow) and IBM RPA (Robotic Process Automation). This has drastically reduced the response time for password resets as well as reduced the number of staff required at the User ID Management Department.
- Fully automated the staff e-loan module, which will help minimise human intervention as the system itself screens applicants to identify eligible requests.
- The introduction, in Treasury, of a Foreign Exchange Rate Request Port, which has been fully integrated with the Treasury system. Instead of calling Treasury, branch personnel can now request rates and receive confirmation over the portal, which has reduced the average time of an FX transaction from approximately 8 minutes to 2 minutes. Plans are underway to create a client interface for this platform and, ultimately, to automate the rate quoting and confirmation process using AI.
- The adoption, in the Card Centre and in Digital Banking, of the industry-leading data-analytics tool Qlick Sense. Both units used this tool to develop real-time digital dashboards to support every-day business decisions with a 360-degree view of the customer.
- Building the host-to-host connectivity and framework for corporate customers. The Bank enabled CAMSO (one of its priority business customers) to integrate smoothly with the Bank’s internal banking systems, allowing for seamless financial transactions.
IT Operations and Security
The Bank places the highest priority on maintaining uninterrupted data services for all stakeholders, managing the increasing vulnerability to cyber-crimes and loss of information, and ensuring preparedness for the future. The IT Support unit monitors and maintains the uptime and SLAs of the entire Branch network for Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Myanmar, and the Maldives, which includes:
The Network & Communication unit is responsible for providing secure and reliable communication channels for all stakeholders, both internal and external, across the entire Branch network. In 2020, the uptime of defined critical systems (Priority 1) of the Data centre was 99.97%, and the uptime of the network was 99.98%.
In 2020, the Bank successfully maintained the PCI DSS and ISO 27001:2103 certifications and was awarded the ISO 20000 certification. The ISO 27001:2013 is a key international standard on information security management, which specifies requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continuously assessing and improving an information security management system. The Bank has successfully maintained ISO 27001 for nearly 10 years.
The Bank has also maintained the prestigious Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) V3.2.1 certification for three consecutive years. PCI-DSS is the global data security standard adopted by payment card brands for all entities that process, store or transmit cardholder data and sensitive authentication data. It is one of the most technical standards and its maintenance requires significant expertise and resources. This certification, which also covers the Bangladesh operations, facilitates the Bank’s rapid card growth while mitigating the risks of security breaches and data theft.
In 2019, the Bank completed the Stage I audit of ISO/IEC 20000 – the most globally recognised standard for exceptional IT Service Management. The Stage II audit was successfully completed in 2020 and the Bank was awarded the ISO/IEC 20000 Practitioner Qualification Certificate. The implementation of this standard will enable the Bank to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the IT Services that are being delivered to the internal and external customers, and allow the Bank to derive more value from its IT investments.
The Bank completed implementation of the Baseline Security Standard in 2020, the outcome of which was the development of Risk Treatment Plans for each department. The Bank also implemented a cutting-edge Anti-Money Laundering (AML) solution for operations in Sri Lanka, the Maldives, and Bangladesh. This initiative is more powerful than the previous AML solution and it enables the Bank to identify AML-related use cases and filters aligned with world standards. In addition, this system is capable of integrating other peripheral systems, most importantly the CBSL GOAML application.