7
Staying on course
Risk management
Introduction
As a financial institution, People’s Leasing is an intermediary between various stakeholders who directly avail financial services or assist us with the provision of such services. Similarly, the business activities of People’s Leasing also lead to transforming maturities of assets and liabilities from short term to long term. These two activities enable People’s Leasing to operate at relatively higher levels of gearing relative to the available capital, well beyond the levels at which corporates in other industries operate. It is this gearing that enables the Company to generate reasonable returns to the shareholders (ROE) despite very low levels of return on assets (ROA). However, such high levels of gearing invariably expose the Company to higher levels of risk as well.
In order to mitigate the risks associated with this business model, People’s Leasing has set up a sound Integrated Risk Management Framework (IRMF). The focus of the IRMF is to manage our exposures to risk and potential losses and to protect the value of our assets and shield earnings. Apart from the compliance requirements set out by the Central Bank of Sri Lanka and other regulatory authorities, we adopt more stringent and dynamic risk management techniques to face the volatile, uncertain, complex and ambiguous (VUCA) environment.
Integrated risk management framework (IRMF)
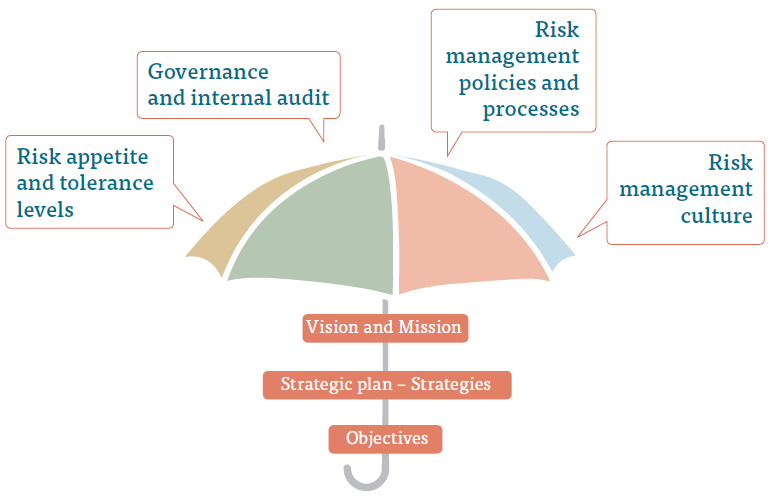
IRMF supports the development and implementation of the risk management strategy of the Organisation. IRMF methodically addresses all the aspects relating to identification, assuming, management, control and reporting of material risks associated with all the activities of the Company within a well defined risk appetite.
IRMF provides for integration of risk management in to the culture of the Company. Commitment of the Board and the best practices adopted in a top down approach translate risk strategy in to tactical and operational objectives and assign risk management responsibilities throughout the Organisation.
IRMF sets out –
- Principal risks faced by People’s Leasing
- Risk appetite
- Roles and responsibilities for risk management
- Risk Committee structure
Principal and emerging risks Principal/Material risks
IRMF identifies the following principal/material risks in relation to the activities of People’s Leasing. As a financial services intermediary, core activities have certain embedded risks which need a dynamic mechanism to identify them in advance.
Identification of the material risks which have an impact on executing strategies of the Company is of utmost importance to People’s Leasing. Uncertainties in the operating environment at both macro and micro levels seriously impact the financial institutions as they amplify the principal risks and their magnitude is higher for us as the largest NBFI in the Sri Lankan Market place. So, People’s Leasing is constantly on alert to these developments and develops and executes strategies to manage risks arising from its core activities.
The following diagram depicts the principal risks and subcategories of risks that affected People’s Leasing during the financial year 2018/19:
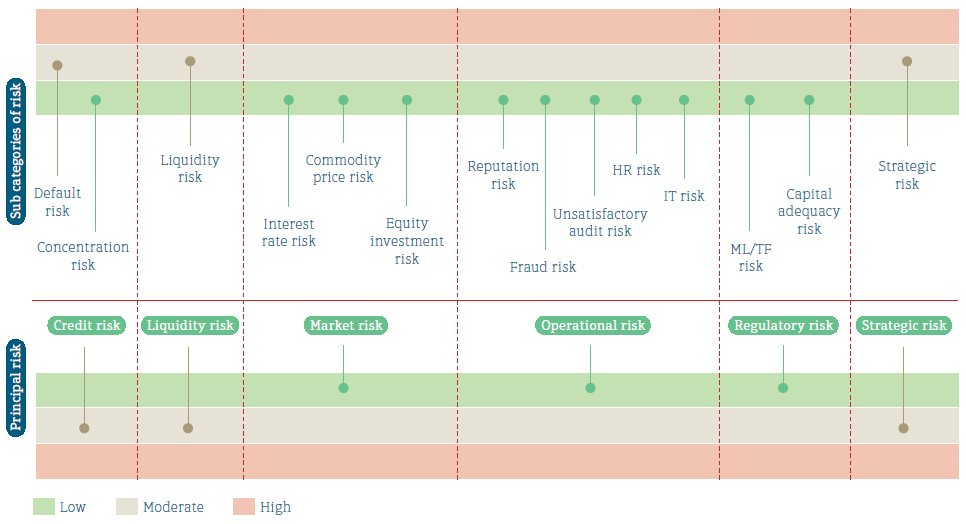
Emerging risks
Besides the conventional risks referred to above, financial institutions are also feeling the impact of several emerging risks arising from certain global and local developments. These include lackluster economic growth, tightening rules, regulations and standards, pervasive trends in information and communication technology, demographic changes, unorthodox competition etc. Some of these risks threaten our conventional intermediary business model and demand us to adapt. Given below is a summary of emerging risks and the actions taken during the financial year 2018/19.
| Risk factor | Nature of the impact | Impact for the Company | Precautions taken |
| Sluggish 3.3% economic growth | Decline in the demand for credit | Sluggish growth in loan book | Managing the margins |
| Low disposable income | Deterioration in asset quality and increasing impairment charges | Strengthening recoveries | |
| Weakening of some of the sectors of the economy |
High delinquencies and limited growth opportunities | Introduction of new products Enhanced the scrutiny level at head office level on identified products | |
| Depreciation of the Rupee/USD |
Restricts imports | 200% LC margins for vehicles leading to less demand for leases | Company focused on registered vehicles |
| Introduction of new IRD Act |
Broadening the WHT base and higher effective tax rate | Lower deposits growth and increase in cash outflows | Effective tax planning and educating customers |
| Debt repayment levy | Higher effective tax rate and impact on profitability | Declining profitability | Focused on revenue growth and revised budgets |
| Increasing policy rates | Impact on the affordability of consumer debt and corporate profitability | Higher borrowing costs and declining profitability | Introduction of variable rate products |
| Collapse of finance companies | Erosion of customer confidence | Lower deposits growth, higher interest costs and declining profitability | Advertising and other activities to promote brand and image and highlighting the strength of credit ratings and the association with the People’s Bank |
| Technological advancements | Challenges to the business model and processes and practices are changing | Competition from fintech solutions and offer of value added services | PLC Online App |
| Introduction of IFRS 9 | Broadening the scope for impairment and more forward looking | Higher impairment provisioning | Tightening credit granting and post sanction monitoring processes |
Risk appetite and tolerance levels
Risk appetite is the level of risk People’s Leasing is ready to take when executing its business strategies. IRMC reviews and sets out the maximum risk tolerance levels annually, being responsive to the changes in operating environment and external factors. Risk and Control Department translates risk tolerance levels in to procedures and protocols to ensure that each risk receives adequate attention when making tactical decisions. At the operational level, risk appetite dictates operational limits and boundaries for routine activities.
| Category | Risk indicator | Maximum Risk tolerance level | Regulatory limit | As at 31.03.2019 % | As at 31.03.2018 % |
| Credit risk | Non-performing (Gross) | <5% | 3.91 | 2.70 | |
| Three months over due | <10% | 7.57 | 4.43 | ||
| Impairment charges | <1.2% | 0.63 | 1.00 | ||
| Concentration Risk | Single borrower Limit | <Rs. 3.2 Billion | 15% capital funds | complied | complied |
| Liquidity Risk | Liquid assets ratio | >100% | 100% | 108.90 | 117.89 |
| Maturity mismatch ratio (Up to one year) | >-45% | -20.04 | -21.55 | ||
| Liquid assets to short term liabilities ratio | >30% | 78.19 | 74.86 | ||
| Market risk | Interest rate sensitivity | <6% | 0.37 | 0.66 | |
| Interest Rate Re pricing Gap | <20% | 7.43 | 11.92 | ||
| Operational Risk | Frauds detected (value as % of Opex) | <0.5% | Nil | Nil | |
| Unsatisfactory Audits (No. of) | <15% | Nil | Nil | ||
| Regulatory Risk | Core capital ratio | >6% | 6% | 14.36 | 18.38 |
| Total risk weighted capital | >12.5% | 10% | 15.20 | 16.46 | |
| Strategic Risk | Return on Equity | >15% | 15.88 | 16.66 | |
| Net interest margin | >7.5% | 9.70 | 8.36 |
Roles and responsibilities for risk management
Risk management at People’s Leasing is embedded in to the organisational culture. Changes in the environment identified and communicated to the employees through introduction of new protocols and amendments to the existing protocols. People’s Leasing has empowered its staff members to act in a precautionary manner and communicated the reporting structure to report risk factors to the Risk Management Department.
People’s Leasing deployed the
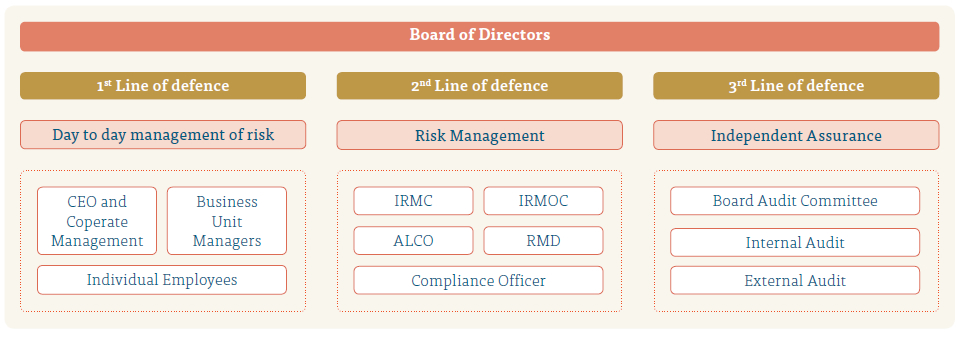
First Line of Defence
First Line of Defence comprises all the employees assuming risk in the revenue generating and client facing areas of the business and all support services functions such as Treasury, HR Department, Finance Department, Marketing etc.
Roles and Responsibilities of 1st Line of defence
- Determine strategic approach to risk and set risk appetite
- Establish the Structure for Risk Management
- Understand the most significant risks to PLC
- Manage organisation
- Build a culture of risk awareness within the organisation.
- Communicate changes in the protocols
- Make sure that risk management policies are implemented
- Communicate feedback on the effectiveness of the implemented policies and areas of improvements
- Understand, accept and implement RM processes
- Report inefficient, unworkable controls
- Cooperate with management
Second Line of Defence
Second line of defence comprises employees of Risks and Compliance functions. Second line of defence sets out policies, procedures and limits for the first line of defence to follow. Setting Risk appetite levels which the first line of defence should act upon is the primary function of this level.
Roles and Responsibilities of 2nd Line of defence
Integrated Risk Manegment Committee (IRMC)
IRMC was setup by the Board by delegating its authorities to develop and oversee Risk Management policies of the company. IRMC functioned as the highest authority in managing the risk of the company. This committee is headed by an Independent Non-Executive Director and includes two other Non-executive directors.
CEO, two SDGMs and DGM risk attended the committee meetings which is held quarterly. As an when required, the other officers have been invited to attend the proceedings.
Assets and Liabilities Committee (ALCO)
This is a management committee which is headed by CEO and attended by the corporate management to mainly look in to the liquidity and interest rate risks of the Company. Apart from this, the Committee looked in to the other day today functions as well.
Integrated Risk Management Operating Committee (IRMOC)
This is Management Level Committee headed by the DGM Risk and Control with the participation of SDGMs operations, DGMs, Chief Managers and Senior Managers and representatives from Risk and Control Department.
Primary objective in revitalizing this committee is to discuss and implement risk mitigation strategies in to the areas of deteriorating credit portfolio and other emerging risks. Apart from this, RCD uses this as a platform to execute guidelines of IRMC and vice versa.
- Develop risk management policy and keep it up to date
- Compile risk reports and report to the Board
- Setting up internal risk policies and structures
Third Line of Defence
Third line of defence represents the Internal Audit function of the Company. Internal Audit reports the effectiveness and the execution of the internal controls and policies and procedures set by the Company. This includes both the internal controls set by the other divisions and the Risk Management Department.
Although Legal Department reported to the Risk Management Department, they are not part of any of the three lines of defence, but they support all departments in the Company including Risk Management Department.
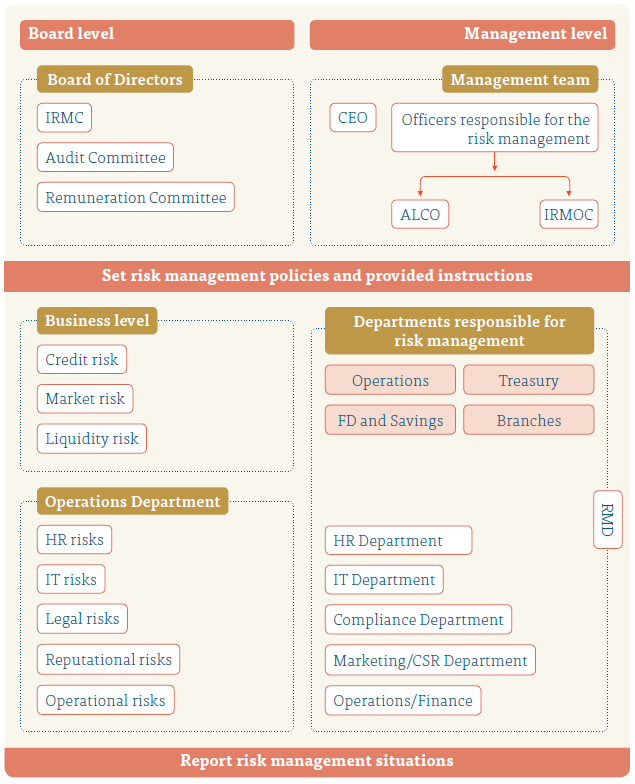
Risk management committees
Risk committees which are appointed by the Board, manage the risk management function via Risk Management Department. Policies and procedures set out by these committees are implemented and monitored via the Risk Management Department.
Principal riskmanagement
Credit risk (CR)
Outline
Credit Risk is the risk arising from failure of the counterparties to honour their financial obligations to the Company in a timely manner. These include principal lent, interest thereon as well as other charges associated therewith. With more than 90% of the assets of the Company representing interest earning assets/lending portfolio, credit risk accounts for 96% of the total risk weighted assets. Hence, the magnitude of the impact of credit risk arising from deterioration in asset quality can be severe for the Company. As a result, People’s Leasing uses robust and dynamic risk management policies and procedures to manage its credit risk. People’s Leasing identified two main components of credit risk viz, default risk, and concentration risk.
Credit risk management
Credit Management at People’s Leasing consists of two facets:
- Disbursement management process
- Default management process
Disbursement management process
People’s Leasing strongly believes that comprehensive and well-articulated credit policy and procedures help overcome high levels of delinquencies. Therefore, People’s Leasing has clearly defined credit policies and approval limits for new disbursements and these guide the day-to-day routine operation of credit to minimise default risk and the concentration risk.
Following factors are taken in to consideration by the Company in managing the credit risk:
- Establishing an appropriate credit risk environment
- Operating under a sound credit granting process
Establishing an appropriate credit risk environment
The Board of Directors sets out the credit risk strategy of the Company. During the financial year 2018/19, Board approved the credit policy drafted by the risk department of the Company. Risk department reviewed the processes and procedures of the Company in relation to credit risk in consultation with the CEO and two Senior DGMs and performed the relevant changes for the credit strategy with the approval of the Board of Directors.
Two Senior DGMs operations, Zonal heads and Branch heads implemented the set credit strategy in day-to-day operations in relation to disbursements, default management and legal documentation aspects. Further to this, RCD reported the risks associated with the product portfolio to the IRMC during the financial year and incorporated suitable amendments to the policies and procedures of the Company.
Operating under a sound credit granting process
People’s Leasing is mainly engaged with the subprime customer base. Hence, the need for stringent credit appraisals to avoid possible losses for the Company cannot be overemphasised.
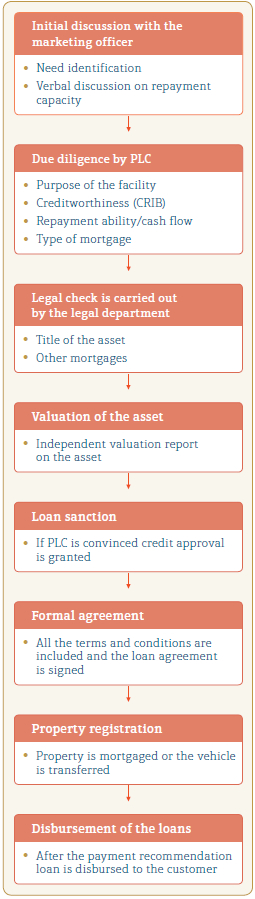
People’s Leasing’s credit granting process is mainly decentralised. Major part of the credit originated at the branch level except margin trading and some of the factoring products. The credit proposals are evaluated and processed based on the credit policy and the operational guidelines of the Company. Key functions in the credit life cycle are depicted in the diagram below:
Key aspects in the credit life cycle of People’s Leasing
People’s Leasing’s risk management policies and procedures make sure that credit risk is managed throughout the life cycle of credit. RCD reviews the process from time to time and effects changes to the policies and procedures with respect to risk exposure limits.

Segregation of duties
Clear segregation of duties in the credit granting process is a key aspect to manage the credit risk at People’s Leasing. Well-articulated credit execution and approval process minimise the risks associated with the credit granting. People’s Leasing has allocated lending officers with different perspectives in to the credit approval process and therefore, each perspective is taken in to consideration when disbursing lending facilities.
RCD provides inputs in managing the credit risk throughout the life-cycle of the lending facility.
Independent risk assessment
and risk treatment
Individual, Corporate and SME facilities are reviewed independently by the different levels based on the disbursement amount of the facility. RCD took part and provided recommendations to the higher approving authorities when the disbursement value exceeded the predefined limits.
Delegation of authorities
Risks of the facilities are verified based on the authority limit assigned to each approving officer ranging from Branch Manager to the SM – Operations, CM – Operations and SDGM – Operations and the CEO. RCD provides credit evaluation throughout the life cycle of the lending facility.
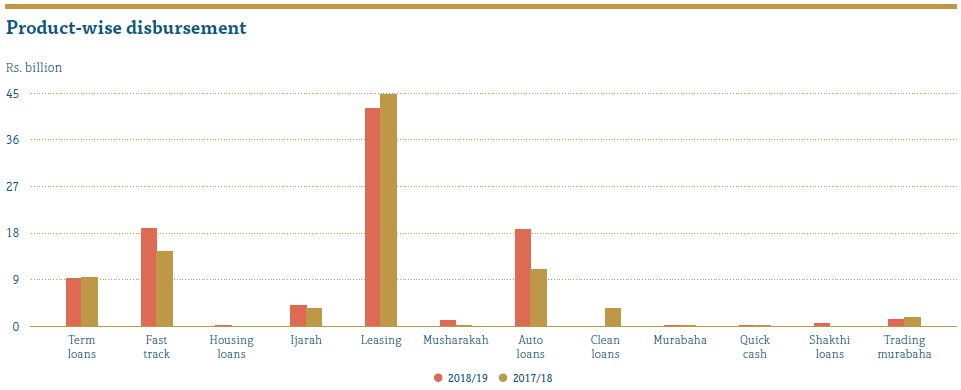
During the year under review, People’s Leasing disbursements increased by 8.46% which stood at Rs. 95.29 billion. Leasing remained the main contributor at 44.01% of the total disbursement of the Company. Fast Track disbursements grew by 31.80% which represents 19% of the total disbursements.
Tougher market conditions due to certain macroprudential developments forced People’s Leasing to follow a more stringent credit appraisal mechanism, leading to a marginal growth in disbursements.
Credit risk mitigation methodologies
People’s Leasing employed a range of techniques and strategies to mitigate
the credit risk of the Company.
They included –
- Netting and set-off
- Collateral
- Risk transfer
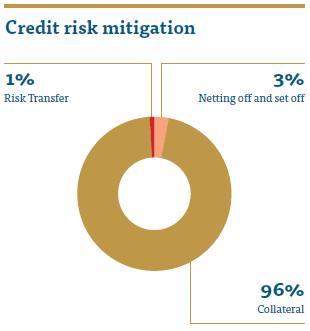
Netting and set off
People’s Leasing adopted this as an effective form of risk management. During the year under review, following product adopted these methods.
Loans against fixed deposits
– SelfeCash
We granted loans up to 80% of the value of the fixed deposit being held by the Company. At the point the loan value exceeds the fixed deposit value, system automatically identifies them and informs respective fixed deposit officer to settle the loan to avoid any default risk.
– Margin trading
People’s Leasing provided margin facilities to purchase shares for the investors.
Once the minimum margin requirement falls based on the stipulated standards, People’s Leasing sold off the shares and recovered the dues.
– Factoring
Factoring product provides working capital requirements for the businesses. People’s Leasing offers factoring, bill discounting, cheque discounting, invoice discounting for corporate, semi-corporate and SME customers. At the point where loan outstanding exceeds 80% of the invoice value People’s Leasing sets off the loan amount from the respective debtor or the payee.
Collateral
People’s Leasing uses collateral as an effective mode of risk management for the loan portfolio. People’s Leasing has the right to call upon the collateral of the counterparty in the event of default. We always make sure that the exposure of a loan is limited to realisation value of the asset at any given point.
- Leases/Ijarah
People’s Leasing provides leasing facility for an underlying asset most probably a vehicle or equipment. We keep the legal rights of the assets and have the right to request for the asset at any given point if the counterparty fails to honour the contractual settlements.
- Auto loans/motor loans
These facilities have been secured with underlying motor vehicles. Although we do not obtain the absolute ownership, we ensure that these vehicles are mortgaged to the Company. As a result, at any given point People’s Leasing can take necessary measures and own the vehicle to recover the outstanding amount.
Risk transfer
A range of instruments including personal guarantees, negotiable documents guarantees, and credit insurance has been used by People’s Leasing to transfer the risk of the counterparty.
Quick loan is designed for the permanent salaried employees without any collateral. This is similar to personal loan. Two guarantors are compulsory as a security for the disbursement of the loan.
Concentration risk
Concentration risk refers to the level of risk our portfolio is exposed to arising from concentration to a single counterparty, sector, product, geography, or industry. Management of the concentration risk is through diversification of the portfolio throughout sectors, industries, customers, and geographies.
IRMC decides the concentration levels for each industry and the single borrower limits. RCD continuously monitors the exposure levels to the management and the IRMC.
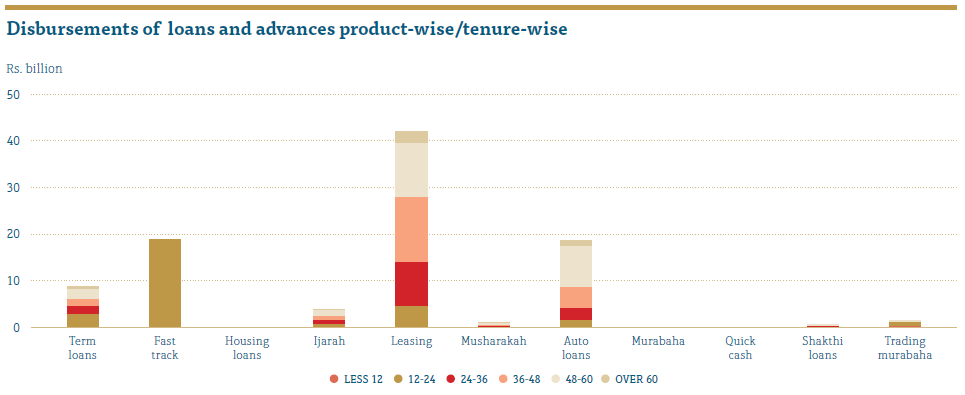
Disbursements during the year mainly concentrated within 12 – 60 months maturities, which accounted for around 95% of the total. We introduced products with extended maturities during the financial year. Granting consists of 3.89% concentrated on above 6 years maturities. Fast Track product concentrated around 12 – 24 months maturities simply because this product has been used for the short-term working capital requirements of the customers.

Our portfolio concentrated mainly on the Western Province and the Leasing product. The Leasing product itself contributed 55% of the portfolio whilst Western Province reflected 47% of the portfolio. RCD closely monitors the security and the Loan to Value Ratio of the Leasing product to minimise the concentration within this product. Diversified portfolio of vehicles, properties, machinery and equipment were taken as collateral and required LTV ratios were maintained.
Default risk (DR)
Default risk is the risk of potential financial loss resulting from the failure of customers/counterparties to meet their debt and contractual obligations.
Default management process
Default risk is the potential financial losses that People’s Leasing may incur due to customer or counter parties failure to meet contractual obligations as agreed.
Default management is one of the key aspects in the People’s Leasing risk management. We have a dedicated Recovery Department headed by a DGM who is responsible for this aspect. Both the Legal Department and the Risk and Control Department assisted the Recovery Department to manage the defaults during the financial year.
Company has a well organised recovery structure based on three pillars –
- Branch Recovery
- Pre-legal
- Legal
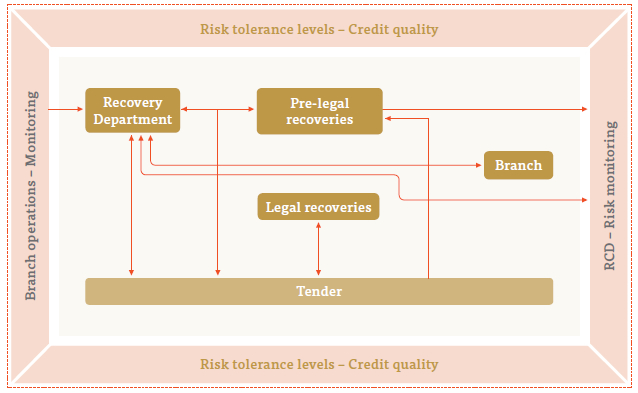
Default risk management and monitoring
Integrated Risk Management Framework of People’s Leasing is well equipped and dynamic to absorb the shocks arising from credit. So, out of the total assets, lending portfolio accounted for a major part of the assets base, which exposes People’s Leasing to default risk by the counterparties.
In terms of profitability, default provision accounted for 3.51% of the profits during the year under review. The Risk and Control Department of the Company assists the two zones and the Recoveries Department with the assistance of the Legal Department to manage the default risk effectively and efficiently.
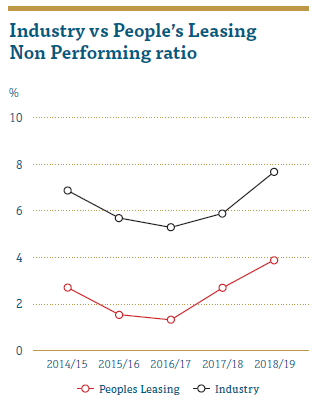
During the year under review, Industry NP ratio as of 31 December 2018 recorded at 7.70% when compared to 5.9% reported in 2017. However, we managed to record 3.91% NP ratio, well below that of the industry but recorded a growth when compared to 2017, which stood at 2.70%.
The main reasons attributable to this increase are unfavourable weather conditions and slowing down of the economic activities during the year. We adopted a sound credit evaluation process and default management techniques which paved the way to manage the non-performing ratio well below the industry.
An assessment of the credit portfolio based on the Risk tolerance levels set by the IRMC, showed that People’s Leasing’s risk profile stood at a moderate. RCD monitors the KRIs on a monthly basis to identify the trends in the NP ratio of the Company and communicated them to the Management.
Adoption of the expected loss model
In line with the SLFRS 9 adoption, losses for impaired loans and receivables are recognised promptly when there is objective evidence. Impairment allowances are calculated on an individual and collective basis. Impairment losses are recorded as charges to the Statement of Profit or Loss. The carrying amount of impaired loans and receivables on the Statement of Financial Position is reduced through the use of impairment allowance accounts. Losses expected from future events are not recognised.
Collective impairment allowance is determined based on the following factors:
- Historical loss in portfolios with similar credit risks
- Impact of current economic conditions over the performance of the credit
Individual impairment allowance is determined based on following factors:
- Significance of the customer exposure
- Any signs of objective evidence of loss
Expected Credit Loss (ECL)
Measurement of ECL involves increased complexity and judgement, including estimation of probabilities of default (PD), loss given default (LDG) and a range of future economic scenarios. Impairment charges will tend to be more volatile and judgemental under SLFRS 9 and will be recognised earlier. Unsecured credit such as clean loans and quick cash are the most impacted.
| ECL | Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Stage 3 | Total |
| Portfolio | 114,902 | 26,640 | 15,109 | 156,652 |
| Impairment | 782 | 616 | 3,547 | 4,944 |
| Ratio (%) | 0.68 | 2.31 | 23.47 | 3.16 |
Days past due for stages 1, 2 and 3 are 0 to 30 days, 30 to 90 days and above 90 days respectively.
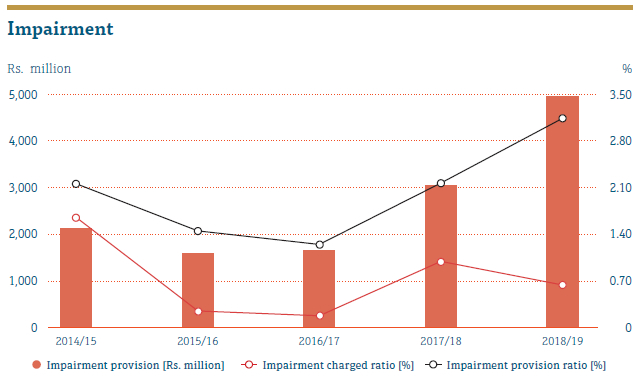
During the financial year 2018/19, impairment provision ratio increased by around 1% due to recognising expected losses as well. This had an impact over the impairment charged ratio too. We recorded a Rs. 993.32 million impairment charge although arrears of the Company declined when compared to the previous year.
RCD of the Company performed stress testing and looked into the impact on the profitability and reported to the IRMC while the Recoveries Department took corrective actions.
Impact of increase in the level of loss ratio| Magnitude of shock (%) | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| Impairment charge to P&L Rs. ’000 | 1,489,981 | 1,707,009 | 1,924,036 |
| Increase in impairment charge Rs. ’000 | 424,054 | 641,081 | 858,108 |
| Return on assets | 3.77 | 3.64 | 3.51 |
Market risk (MR)
Market risk refers to the risk of loss arising from the potential adverse changes to the values of the Company’s assets and liabilities from the fluctuations in market variables including but not limited to interest rates, equity prices, foreign exchange rates, and commodity prices.
Managing the market risk
Integrated Risk Management Framework contains well-articulated policies and procedures to manage the market risk. Major part of our assets and liabilities are at book balance which represents 99% of the total assets and 100% of the total liabilities. RCD has been reporting to IRMC and the Management based on market risk policies, tolerance limits, and market triggers. Monthly ALCO meetings which are organised to review mainly the interest rate risk reviewed and adjusted the lending and borrowing rates to minimise the possible adverse impact.
Composition of the balance sheet in terms of trading and non-trading portfolio
| As at 31 March 2019 | Trading book Rs. million | Non-trading book Rs. million |
|
|
||
| Cash and cash equivalents | 3,294 | |
| Balances with banks | 3,405 | |
| Financial assets – held for trading | 23 | – |
| Loans and receivables | – | 151,708 |
| Financial assets – OCI | 125 | – |
| Debt instruments | – | 8,002 |
| Investment in subsidiary | – | 3,213 |
| Investment in associate | – | 238 |
| PPE and other assets | – | 2,532 |
| Total assets | 148 | 172,393 |
|
|
||
| Due to banks | – | 27,274 |
| Due to customers | – | 88,369 |
| Debt securities issued | – | 21,275 |
| Other financial liabilities | – | 7,020 |
| Shareholders’ funds | – | 28,603 |
| Total liabilities | – | 172,541 |
The trading book represents the assets held by the Company with the intention of trading whilst the non-trading portfolio represents the assets held without any trading intent. The table below shows People’s Leasing’s assets which were prone to market risk and assets which did not involve any market risk.
Interest rate risk
The risk that a firm is exposed to capital or income volatility because of interest rate exposures of assets and liabilities. Along with the gradual increase in the interest rates during the year, our interest risk increased slightly. RCD closely monitored and evaluated the magnitude of risk through stress testing and monitoring tolerance levels and reported to the IRMC and the Management.
Interest rate sensitivity analysis gap (’000)
The table below depicts the interest rate risk exposure at People’s Leasing on its non-trading financial assets and liabilities. Assets and liabilities are at their carrying amounts in the balance sheet categorised in to each band based on the contractual re-pricing point.
| Description | On demand | Less than 3 months | 3 to 12 months | 1 to 3 years | 3 to 5 years | Over 5 years |
| Financial assets | 8,636 | 25,342 | 49,023 | 65,998 | 19,344 | 80 |
| Financial liabilities | 11,452 | 35,903 | 46,535 | 27,651 | 15,255 | 119 |
| Interest rate sensitivity gap | (2815) | (10,562) | 2,487 | 38,346 | 4,089 | (39) |
Stress test on NII on the interest rate shock
The table below depicts the magnitude of the impact of the fluctuations in the market rates on the earnings of People’s Leasing. Fluctuations in the market rates affected the profitability of the Company and not the market values of the products.
Upward trend in the market interest rates increases the funding cost of the Company, in the areas of fixed deposits and savings as well as funding through debt instruments. Based on the movements in the AWPLR and the predictions and perceptions, RCD performs stress testing and updates the Management and the IRMC about the potential impact.
| Impact on NII | 2019 | 2018 | ||
| Rs. ’000 | Increase | Decrease | Increase | Decrease |
| 1% | (53,540) | 53,540 | (94,953) | 94,953 |
| 3% | (160,619) | 160,619 | (284,860) | 284,860 |
| 5% | (267,698) | 267,698 | (474,766) | 474,766 |
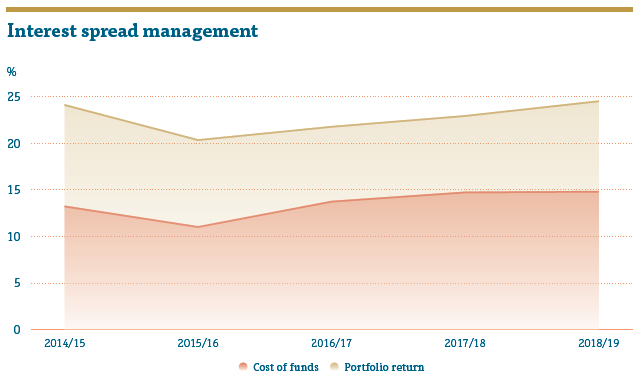
We took timely steps to manage the interest spread during the year. RCD provided the necessary guidance to the Management about the trends of the market interest rates and their impact on the profitability through stress testing. ALCO meets monthly and decides the lending and borrowing rates of the Company. The Graph below depicts the portfolio return and the cost of funds during the year. It was evident that People’s Leasing took timely steps to manage the profitability by exploiting the fluctuations in the market. People’s Leasing introduced variable rate loans to tackle the interest rate risk.
Commodity price risk
This is the uncertainty that adversely impacts the financial results of the company due to change in Gold prices. PLC commenced gold loan facilities to the customers with the aim of providing extended facilities under one roof. RCD closely monitors the fluctuations in the Gold prices in the world market. People’s Leasing adopted a LTV on the maximum loan amount which is mainly based on the Gold prices, purity and the weight of gold content.
ALCO will decide the LTV and adjust the loan quantum per gram price. Although exposure is not material in current context, RCD closely monitors the Gold price movements in the market and advises the management accordingly.
Equity price risk
Equity price risk is the risk that the fair value of equities may decrease as a result of changes in levels of equity indices and the value of individual stock. Market exposure of the PLC over the equity interest is negligible. However, ALCO monitored the equity investment values against the stop loss limit. The equity investment portfolio recorded a market value of Rs. 148.83 million as at 31 March 2019 (refer page 366).
Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk refers to the inability of a firm to settle its financial obligations, without having to incur major losses. This usually happens due to mismatches in the maturities of assets and liabilities and the inability to convert assets in to cash without incurring losses. People’s Leasing maintains its liquidity in excess of regulatory requirements. RCD continuously monitors the liquid assets position of People’s Leasing and reports any deviations to the Management.
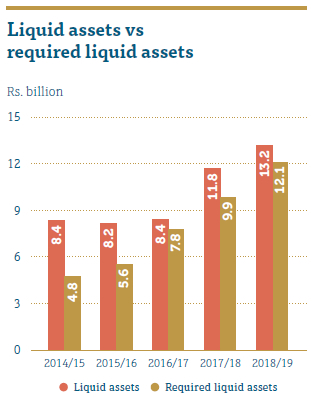
As a financial intermediary, People’s Leasing is inherently vulnerable to this risk. This creates a mismatch between assets and liabilities. RCD continuously monitors the maturity mismatches and reports to the ALCO and the IRMC.
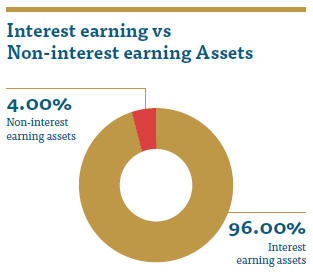
As per the graph, 96% of the Company’s assets represent interest earning assets with only 4% being in non-interest earning assets. Main component of the non-interest earning assets represents the land and buildings. The Company maintains a portfolio of highly marketable and diverse assets that can be easily liquidated in the event of an unforeseen interruption to cash flows. The Company also has committed lines of credit that it can access to meet liquidity needs in the event of any contingency.
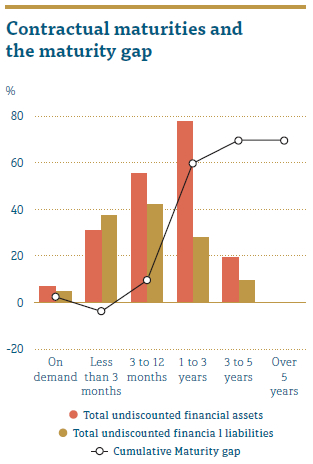
People’s Leasing was able to manage the funding requirements for the business cycle with minimal gaps during the year. Except for in the less than three-month bucket, People’s Leasing was able to manage the funding with positive liquidity position on the contractual cash flow maturities in all other buckets.
Funding structure
By adopting sound liquidity risk management practices, we were able to monitor and adjust its funding structure in a manner that exerted least pressure on the liquidity position of the Company. During the financial year, People’s Leasing mainly focused on long-term fixed deposits and savings, with less focus on bank borrowings. Credit rating plays a critical role in sourcing funds for the Company. People’s Leasing managed to retain international rating of B- from Fitch Rating International.
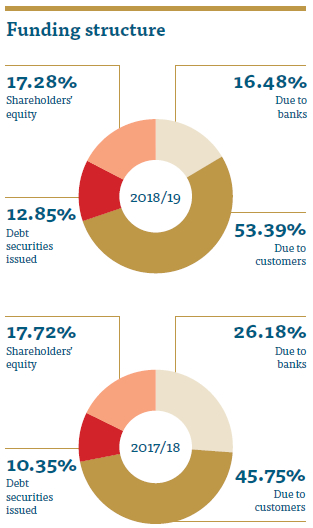
People’s Leasing funding strategy is more focused on customer deposits. Excess liquidity in the market enabled us to source low cost funding with longer maturities directly from the customers. On the other hand, bank borrowings and the debt securities market preferred shorter tenures due to uncertainties in the market.
Operational risk
The risk of loss to the Company arising from inadequate or failed processes or systems, human factors or due to external events where the root cause was not due to market or credit risks.
Like for any other organisation, operational risks are inherent to People’s Leasing as well. Our objective is to manage it in a more cost effective manner or to eliminate those risks wherever possible without affecting the Company. Our operational risk management framework is a set of guidelines issued by the Company to identify, manage and report possible operational risks.
Operational risks at People’s Leasing comprise following aspects:
- Physical security and premises
- Data management and information technology
- People-related risks and supplier risks
- Cash management and fraud
- Natural disasters and other external events
Operational risk mitigation
Strong internal control framework
People’s Leasing put in place robust and sound internal control framework with well-articulated segregation of duties, policies, procedures. This includes both the IT related controls and manual controls. Audit assignment makes sure the adherence to the laid down policies and procedures. Internal audit, external audit and RCD makes sure the efficiency and effectiveness of internal controls.
Physical security and premises risks
People’s Leasing has clear policies and procedures related to the security of its personnel and physical assets. We adopted policy frameworks for property acquisition and disposal during the year under review. Logistic Department of the Company monitors the implementation of these guidelines. The security of the Company has been outsourced to a third party.
Apart from this, People’s Leasing operates CCTV, with a policy adopted by Board and operational guidelines and procedures for effective utilisation with the assistance of ICT Department of the Company.
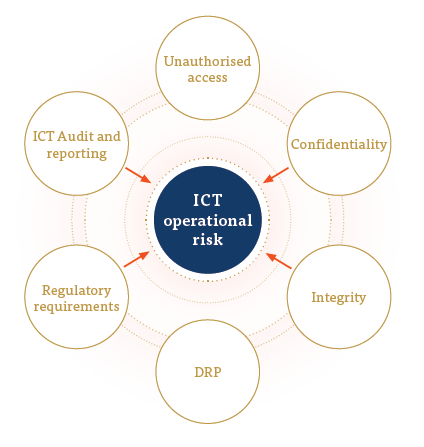
Data management and information technology
Data management and information technology are key aspects in the operational risk management framework at People’s Leasing. We have introduced and modified an Information Security Policy to mitigate the growing risks faced by the Company in this regard. Sensitive information related to customers is available within our system. Being one of the largest NBFI in the market, Our core systems and data base of customer information are highly sought after assets. So, operational risk on information technology is an area where we need to focus a lot on.
Well-articulated policies and procedures followed by different authority levels and clear segregation of duties have been implemented by the Company to avoid information loss and financial loss. During the year under review, there were no reported incidents involving loss of data.
People-related risks
Set of risks faced by People’s Leasing due to employing and managing people. Key functions related to Human Resource Management expose the Company to certain risks, some of which may be regulatory. Since People’s Leasing is operating in a highly regulatory industry with a lot of on-site and off-site surveillance by the Central Bank of Sri Lanka, People’s Leasing needs to attract and retain the best talent to ensure compliance and undertake its business activities responsibly within the Organisation.
Retained people need to be equipped with latest knowledge about systems, processes and regulatory environment, more importantly, on the customer handling and interactions. This specific area has high correlation to other risk aspects as well.
So, People’s Leasing maintained a high focus on this aspect.
During the year under review, employee rotation and compulsory leave policy has been introduced to identify possible operational risks and malpractices. Please refer page 112 for HR related reports.
Payment process and fraud related risks
The risks of related to payments may arise from processing delays or effecting payments without appropriate authentication and proper authorisation. Lapses may occur throughout the process from initiation of the payment process to the external settlement. This function is solely handled by the Finance Department of the Company. The payment function has been centralised at the head office but the initiation of the payment may occur at branch level. People’s Leasing provided different methods of settlements for the customers such as cash, cheque and SLIPS. People’s Leasing has laid down clear segregation of duties and authority levels and approval levels. Payment processing is done at the head office within the Finance Department. Payments are independently verified for their authenticity. The cashier function is held at the branches under the purview of the branch manager, second officer and cash officers. Internal Audit Department carries out ad hoc audits and cash counts to deter and detect malpractices, since People’s Leasing has identified the aspects of cash management as a vulnerable area and prone to frauds and malpractices.
Fraud risk identified as financial loss when internal and external parties act dishonestly with the intent of getting undue benefit which may cause losses to the Company or its customers. During the year under review, RCD reported nine incidents of fraud, to the IRMC.
Natural disasters and other external events
Natural disasters and other external events which are beyond the control of the Company and hence, unavoidable may have an impact on the value of its assets. People’s Leasing has transferred such risks to insurance companies by adequately insuring all its assets against such events.
In the event of such a situation, People’s Leasing has developed a comprehensive Business Continuity Plan in compliance with the professional practices prescribed by the Disaster Recovery Institute International of USA. RCD reviews the implementation plan, operational controls and training to function at a point of disaster. IRMC quarterly reviews the progress.
Regulatory risks
This refers to the potential risks People’s Leasing may face due to non-compliance with the applicable legal and regulatory requirements or contractual obligations. This may lead to reprimanding, sanctions or even imposition of penalties for the Company which may in turn adversely impact its business operations and cause financial losses for the Company. People’s Leasing has a dedicated department headed by the Senior Manager Compliance who is an Attorney-at-Law. Apart from the Compliance Department, Legal and Finance Departments of the Company too contributed towards compliance function of the Company.
Reputation risk
Reputation risk is the losses that People’s Leasing is prone due to actions, transactions, investment or events that will impair the trust, integrity and competence by the customers, clients, counterparties, employees, regulators or the general public.
People’s Leasing maintained a controlled culture within the organisation and a code of ethics has been implemented. Any deviation on acting upon them will subject those responsible to disciplinary actions.
People’s Leasing employees need to act in good faith and maintain integrity in their actions. Marketing department of the Company invested in the CSR activities that benefited the society from whom we earned a considerable portion of our profit. Please refer Embodying Responsible Stewardship section on pages 130 to 145 for further details.
Money laundering and terrorist financing (ML/TF) risks
Money laundering and Terrorist Financing (ML/TF) is considered as a key risk faced by the NBFI Sector in Sri Lanka. Central Bank stipulated rules and guidelines have been issued to the NBFI sector which need to be complied by PLC as well.
Compliance department is closely monitoring any triggering events related to the ML and TF. PLC took measures to screen the Loans and Leases, Fixed deposits and savings in this regard though an automated customer screening and Anti Money laundering applications. During the year under review, no suspicious transactions were reported.
Strategic risk
These are uncertainties or losses arising from fundamental decisions taken by the management in respect of organizational objectives. Essentially at PLC strategic risks are the risks of failing to achieve business objectives.
Board set KPIs for the Company through strategic plan and the Annual budget of the company by aligning Vision, mission of the Company. Board evaluates the company performance based on the set KPIs. RMD closely monitors the developments and reports to the management and the Board on the areas with high risks. So, Board can take corrective actions and put the Company on track if any deviations are noted.
Capital adequacy
Financial intermediaries need to be resilient to the external and internal shocks and hence, sufficient Capital Adequacy is of paramount importance. Regulations have been introduced to avoid non-banking financial institutions failures, to promote stability in the sector, safety and soundness of the system, to prevent systematic disaster and ultimately reduce the losses to the non-banking institution depositors.
New Capital Adequacy Framework for LFCs has been introduced with a view to fostering a strong emphasis on risk management and to encourage improvements in LFCs risk assessment capabilities. People’s Leasing recorded a Tier 1 Capital Adequacy Ratio at 14.36%, well above the regulatory requirement of 6% whereas Tier II capital ratio was recorded at 15.20%.
| Item | 2019 Rs. ’000 | 2018* Rs. ’000 |
| Tier 1 capital | 26,517,785 | 26,515,109 |
| Total capital | 28,065,758 | 23,733,489 |
| Total risk-weighted amount | 184,632,632 | 144,222,712 |
| Total risk-weighted amount for credit risk |
163,078,710 | – |
| risk-weighted amount for operational risk | 21,553,922 | – |
| Tier 1 ratio (%) | 14.36 | 18.38 |
| Total capital ratio (%) | 15.20 | 16.46 |
*Capital adequacy ratio computed and reported based on the previous CBSL guidelines.